Chronic Myeloid Leukemia is a clonal myeloproliferative disorder of the primitive hematopoetic stem cell.
CML is characterized by the presence of the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene on the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph+).
Philadelphia chromosome (Ph+)
- Reciprocal exchange of DNA between chromosomes 9 and 22; t(9;22)
- Results in BCR-ABL fusion protein
- Production of abnormal tyrosine kinase protein
90-95% of cases have the characteristic t(9;22) Ph+
Ph+ cannot be identified in conventional cytogenetic analysis in 5-10% of patients, these will have complex or cryptic (hidden) abnormalities resulting in the same protein formation.
Ionizing radiation is the only environmental factor associated with CML etiology. Only 5-7% of CML patients documented excessive exposure to radiation. There is no known inherited disposition.
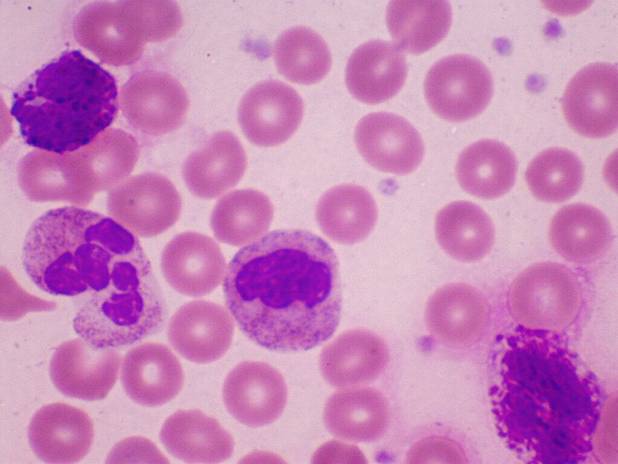
Peripheral Blood Film in CML showing blast cells: