Ewing sarcoma (ES) is a primary malignant bone tumor and is a "small round blue cell" tumor.
The slide below shows malignant Ewing sarcoma cells:
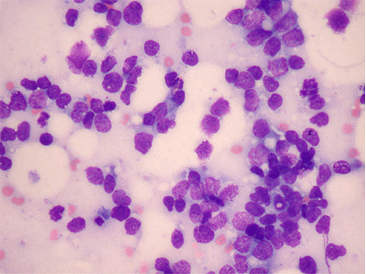
This sarcoma was first described by James Ewing in the 1920s. He was the first Professor of Pathology at Cornell University. He co-founded the American Society for the Control of Cancer (now the American Cancer Society) and was responsible for the foundation of the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Centre. He was also a leading early proponent of radiation therapy in the treatment of cancer.

Also see Professor James Ewing as shown on the cover of Time magazine in 1931
Incidence
Ewing sarcoma (ES) is the second most common primary bone tumor in children (osteosarcomas slightly more frequent).
The etiology is unknown.
- Constitutes 3-5% of all pediatric neoplasms.
- Incidence is about 2 -3 per million children (under age 15) per year.
- The median age of onset is 14 years - usually occurs in teenage years (very rare under age 5 and adults over 30.
- The average age of onset is typically 3-4 years younger in girls, corresponding to their earlier onset of puberty.
- In Canada, between 2001 and 2005, 80 children were diagnosed with Ewings sarcoma between the ages of 0 and 14 years.
Age of Onset of ES:
| Age | Proportion of Ewing Sarcoma |
| Pubertal range | 40% |
| <10 years | 30% |
| >20 years | 5% |
- Male predominance with a male:female ratio of 1.5-2:1.
- Most patients under age 10 are female. ES is extremely rare in individuals of African and Chinese descent.
Summary of Incidence of ES:
| Incidence | 2 -3 per million children |
| Proportion of Pediatric Neoplasms | 3-5% |
| Proportion of Primary Bone Tumors | 6-8% Second most common bone tumor |
| Median Age of Onset | 14 yrs |
| Gender Bias | 1.5-2:1 (male predominance) |
| Racial Bias | Very rare in black and Chinese populations |

