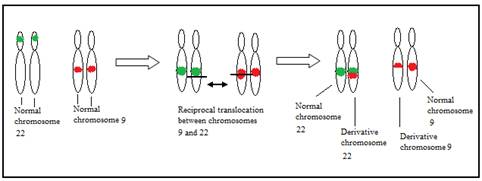
The characteristic abnormality in CML is t(9;22)(q34;q11.2)
- The classic t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) rearrangement occurs in 90-95% of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
- Translocation also seen in up to 25% of adult cases of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL).
- t(9;22) results in fusion of the ABL (Abelson) proto-oncogene on 9q34 and the BCR (Breakpoint Cluster Region) gene on 22q11.2
- Specifically, the 3’ sequences of the ABL gene are translocated next to the 5’ exons of the BCR gene.
- The derivative chromosome 22, which carries the BCR-ABL fusion, is known as the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph).
- The BCR-ABL fusion gene may encode one of two different fusion products depending on the location of the translocation breakpoint in the BCR gene.
- In the majority of CML cases, the breakpoint occurs in an area known as the major breakpoint cluster region (M-bcr).
- The resulting fusion protein is 210kd in size (p210).
- Alternatively, the breakpoint may also occur in an area known as the minor breakpoint cluster region (m-bcr). In this case, the fusion product is 190kd in size (p190).
- The type of fusion product does not appear to have any prognostic significance.
The BCR gene is:
- Ubiquitously expressed
- Encodes a large protein of unknown function.
The ABL gene:
- Encodes a non-receptor tyrosine kinase, which is involved in signal transduction and regulation of cell proliferation.
- Normally, the expression of the ABL gene is tightly regulated.
When the BCR gene is fused with ABL, the tyrosine kinase is constitutively expressed and the activity of the protein is increased.
The BCR-ABL protein appears to be directly involved in the pathogenesis of CML.
At present, the standard frontline therapy for CML is the oral medication imatinib mesylate (Gleevec). Imatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which targets the BCR-ABL fusion protein.
Imatinib has decreased side effects and increased complete response compared to previous drugs and confers a 70-90% response rate with 5-year overall survival between 80 and 95%. The otherwise natural history has a median survival time of 2-3 years.
More detailed information on cytogenetics of CML may be found at:
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology

