Intrathecal chemotherapy
- All Treatment phases
- IT Cytarabine
- IT Methotrexate
IV chemotherapy
- High dose IV Methotrexate
- Cytarabine
PO chemotherapy
- Steroids (Dex vs Pred)
Prophylactic Cranial Radiation Therapy (RT)
- Considered for high risk patients only:
- T cell leukemia
- High WBC count at presentation ( >50,000)
- Poor responders - patients who have evidence of minimal residual disease with more than 10(-2) residual blasts at the end of induction and prior to their first dose of IV methotrexate.
- Most children with ALL will not require cranial RT, however data from the BFM group recently showed that cranial RT of 12 Gy in 8 fractions plus IT chemotherapy was adequate CNS prophylaxis for children with newly diagnosed high risk ALL.
Treatment Planning
Target volume = entire brain and meninges, including frontal lobe as well as the cribriform place and posterior halves of globes of eyes, with optic disk and nerve.
Field borders:
- Cranial: clear vertex of the skull
- Caudal: at the bottom of the C2 vertebral body
- Anterior: clear the frontal lobe
- MLC blocking is used to shield the anterior globes and facial structures anteriorly and inferiorly
- Care is taken to avoid shielding the cribriform plate
- Posterior: clear the occiput
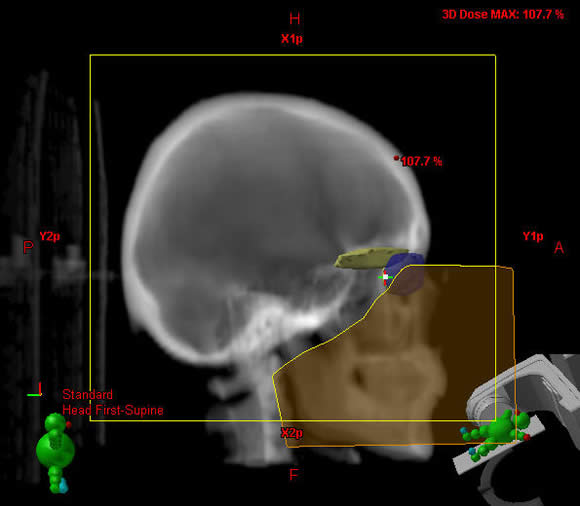
Prescription point is at or near the center of the cranial volume. This is often placed at the anterior block edge in the orbits to minimize divergence into the contralateral globe. This works ideally when the head is not rotated such that the globes at lined up perfectly on the lateral DRR. But if they do not line up, the midpoint is taken between the block edges of the 2 orbits.
The dose generally used is 12 Gy in 8 fractions

