There is usually a short history of symptoms as these tumors are rapidly growing.
Children may present with:
- Signs and symptoms of raised intracranial pressure
- Localizing signs
- Non-localizing signs
General Overview of Supratentorial PNET Presentation:
| Problem | Possible Presentation |
Headache, vomiting, lethargy |
|
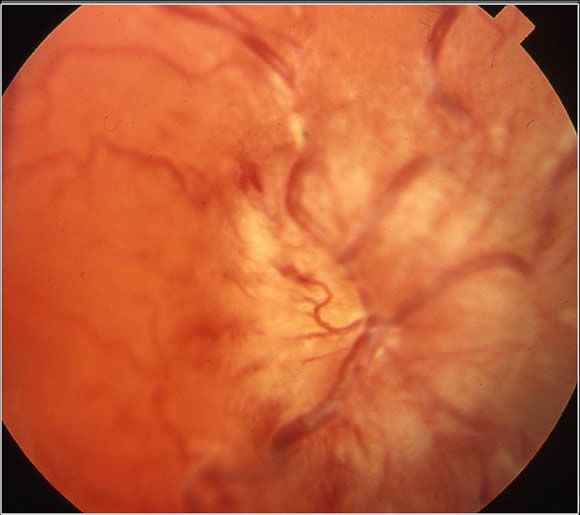
Papilledema - with swelling and hemorrhage of the optic disc on fundoscopy:
|
|
Cranial nerve abnormalities:
The most commonly 6th (VI) - cranial nerve:
This is a "false localizing sign".
Hydrocephalus causes compression of the 6th cranial nerve at the petroclival ligament, resulting in diplopia, medial deviation of the affected eye and lateral gaze paresis.
Left lateral rectus (6th cranial nerve palsy) |
|
Localizing symptoms and signs due to tumor infiltration into normal structures |
Supratentorial brain:
|
Deep midline tumors:
|
|
| Non-localizing symptoms and signs | Seizures General malaise Changes in behavior Loss of previously acquired developmental milestones |