Pineal tumors are very rare (less than1% of intracranial tumors in adults, and 5-10% in children).
- Up to 60% of pineal tumors are germinomas.
- These tumors are slightly more common in males and almost always occur within 10 years of puberty.
- Germ cell tumors may also occur in the suprasellar region.
For pineal germ cell tumors there appear to be 3 principle age groups where peak incidences are found:
- Infancy: 0-3 years
- Adolescence/ young adulthood: 10-30 years (commonest between 10 and 13 years)
- Middle adult life
There is a marked increase in incidence of pineal tumors in Japan (16% of all CNS tumors are pineal tumors).
A higher proportion of these tumors are germ cell tumors as well, in comparison to other parts of the world.
This correlates with the higher proportion of testicular germ cell tumors that are also found in Japan. There is no known reason for this difference.
Different pineal tumor characteristics:
Proportion of adults intracranial tumors |
<1% |
Proportion of pediatric intracranial tumors |
5-10% |
Proportion of germ cell origin |
60% |
Proportion in patients between 10-21 years |
70% |
Proportion in patients <35 years |
95% |
Average age of incidence |
13 years old |
Gender Bias |
3:1 male predominance |
Geographic Bias |
Japan: incidence of 16% |
The relative proportion of pineal region tumors accounted for by each tumor type:
Benign lesions (teratoma, pineocytoma, meningioma) |
30-40% |
Germ cell tumors |
60% |
Glial tumor |
25% |
Ependymal tumor |
15% |
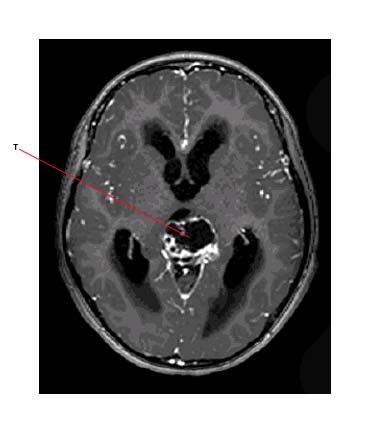
The image below shows a tumor (T) which is a mixed teratoma and germinoma of the pineal region:
External Link:

