Radiology
A chest X-ray is generally the first investigation.
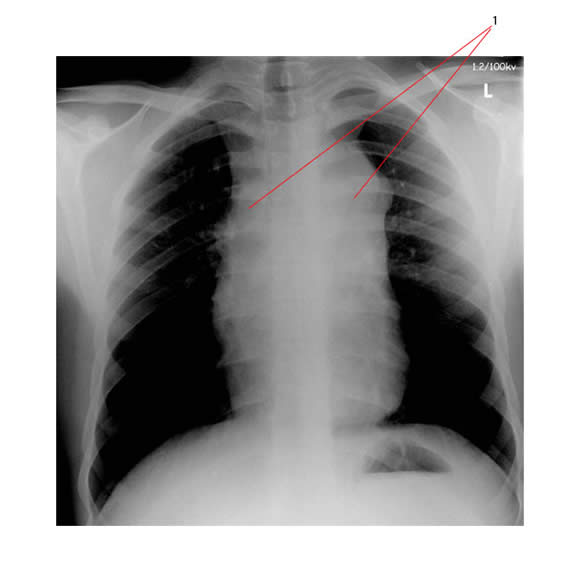
The PA chest X-ray below shows widening of the upper mediastinum (#1) consistent with lymphadenopathy.
The lateral view of the same patient shows loss of the retro-sternal airspace (#2) which is consistent with anterior mediastinal adenopathy.
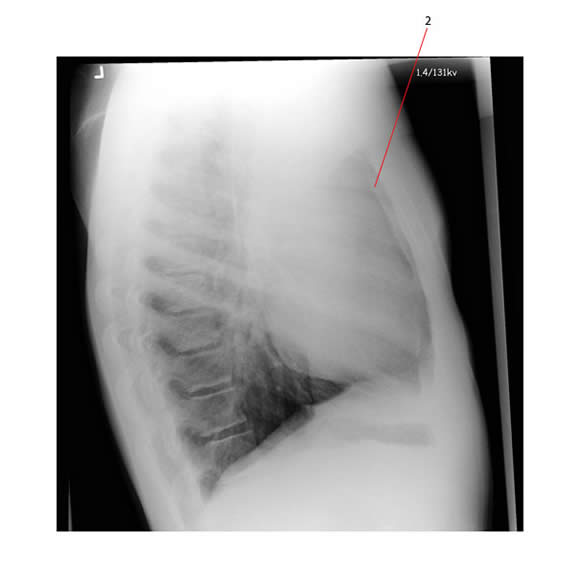
This patient had Hodgkin lymphoma associated with anterior mediastinal disease.
CT scans give important information, but in many centers now an initial CT-PET scan has replaced CT alone. CT-PET scans are an essential part of initial staging and monitoring response to therapy.
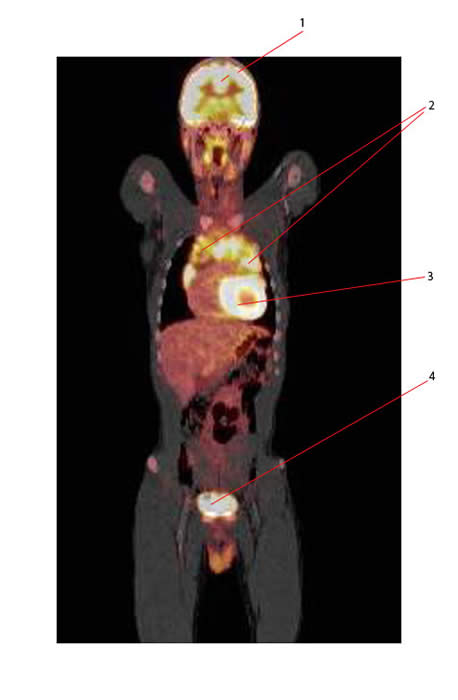
Below is the CT-PET of the same patient whose CXR showed the anterior mediastinal mass:
Structures seen:
- 1: Normal brain
- 2: Mediastinal adenopathy secondary to Hodgkin Lymphoma
- 3: Normal heart
- 4: Normal bladder
Radiological tools for assessing Hodgkin lymphoma:
Description and Function |
|
Chest X-ray |
Posterioanterior (PA) and lateral projections required Important in determining the bulk of the mediastinal lymphadenopathy
Traditionally this means calculating the ratio of maximum diameter of the mediastinal mass to maximum intrathoracic diameter:
|
CT |
Evaluates initial extent of disease Chest scan:
Abdominal and pelvic scans:
|
| FDG-PET | Important investigation to assess extent of initial disease and monitor response to therapy :
Significant advantages over gallium.
|
| Gallium-67 scan | Identify sites of involvement (especially head and neck)
Limitations1:
|
MRI |
Very rarely used in the evaluation of Hodgkin lymphoma.
Chest scan:
Abdomen scan:
|

