Local
- Medulloblastomas arise most often in the midline cerebellar vermis.
- Tumor usually grows to fill the 4th ventricle, and commonly involves the brachium pontis and extends onto the ventricular floor (i.e. the brainstem).
- Medulloblastomas may grow to fill the entire posterior fossa, invading other CNS structures.
- Unlike ependymomas they do not tend to extend through the foramina of Luschka.
The image below shows a large midline posterior fossa tumor (T) - this is a medulloblastoma.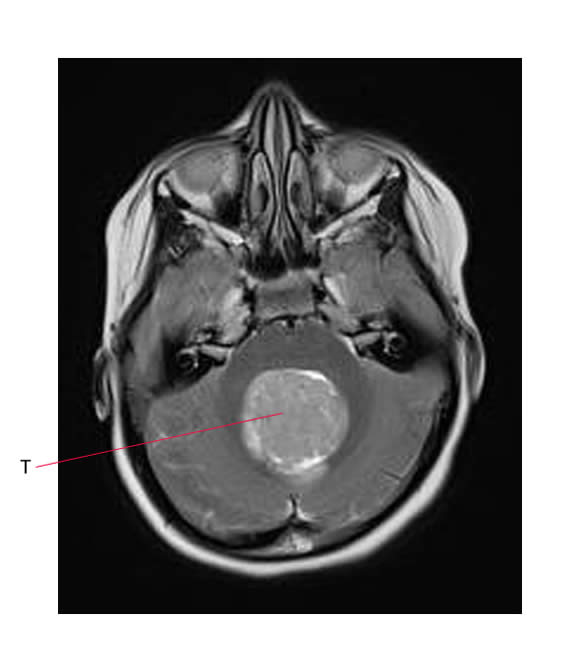
Distant
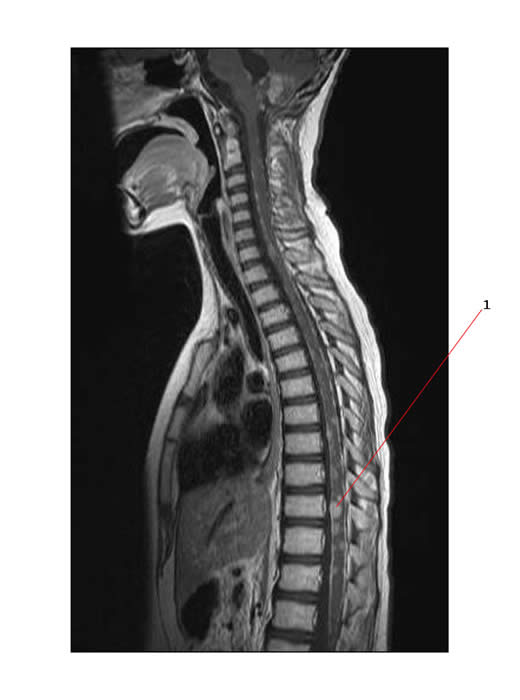
- Widespread seeding of the subarachnoid space may occur (risk of this is 10 - 45%).
- Spinal leptomeningeal disease, appears in about 30% of cases at presentation.
- Intracranial metastasis are less common.
- Distant metastases are rare but may occur in bone marrow/bone.
The MR below shows multiple nodules of metastatic disease involving the subarachnoid space in a child's spine. #1 points to a large nodule.
Summary of Patterns of Medulloblastoma Spread:
| Local |
|
| CSF |
|
| Hematogeneous |
|
| VP Shunt |
|

