Medulloblastomas are embryonal neoplasms.
These tumors are all composed of small round blue cells.
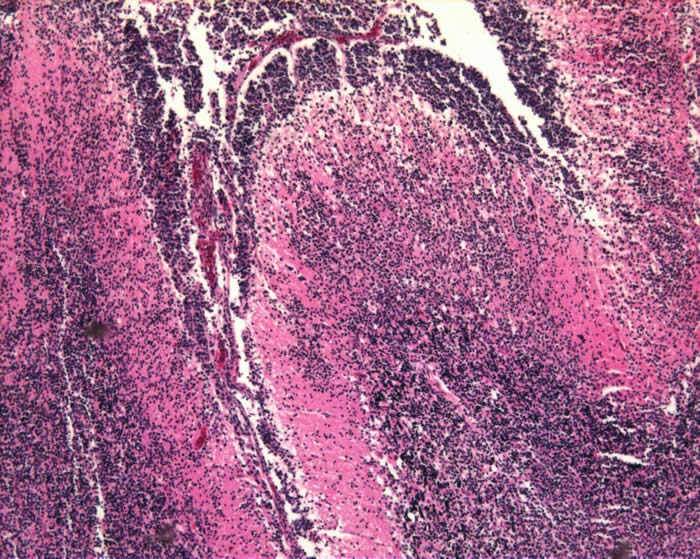
Medulloblastoma arise in the posterior fossa, generally in the cerebellar midline.
Cellular Origin:
- The cellular origin of medulloblastoma remains controversial.
- There are currently two dominant hypotheses as to the origin (see table below).
Postulated cellular origins of medulloblastoma:
| Proposed cellular origin | Evidence |
External granular layer of the cerebellum |
|
Posterior medullary velum |
|
Cytogenetics:
The commonest specific abnormality in medulloblastoma (present in about 50 %), is isochromosome 17q [i(17q)].
See Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
Tumor Histology:
| Location | Cerebellar vermis or cerebellar hemispheres |
Cell density |
Densely cellular |
Nuclear characteristics |
Round, oval or angulated (‘carrot-shaped’) |
Vascular features |
Low vascular density |
Cellular patterns |
Sheets
|
Cell differentiation |
Common
Less common:
(“medullomyoblastoma”) |
Classic medulloblastoma is a highly cellular tumor
- Composed of cells with round, oval or angulated (‘carrot-shaped’) nuclei and minimal cytoplasm.
- The tumor cells are in sheets, rows or nodules.
- Homer-Wright rosettes are present in <40% of cases and consist of nuclei of rosette forming cells arranged in a circular fashion around fibrillary processes.
- Medulloblastomas are mitotically active tumors, often show single cell necrosis and less commonly geographical areas of necrosis.
- Occasionally multinucleated giant cells or cells with large nuclei are seen within the tumor.
Classic hypercellular medulloblastoma with several mitotic figures:
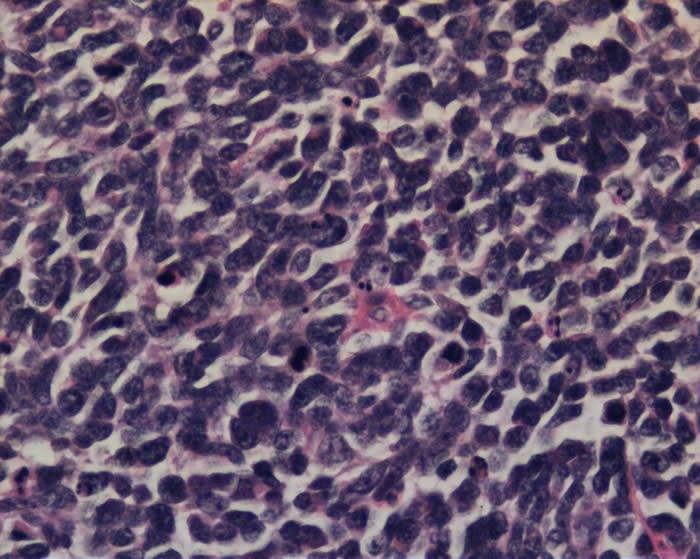
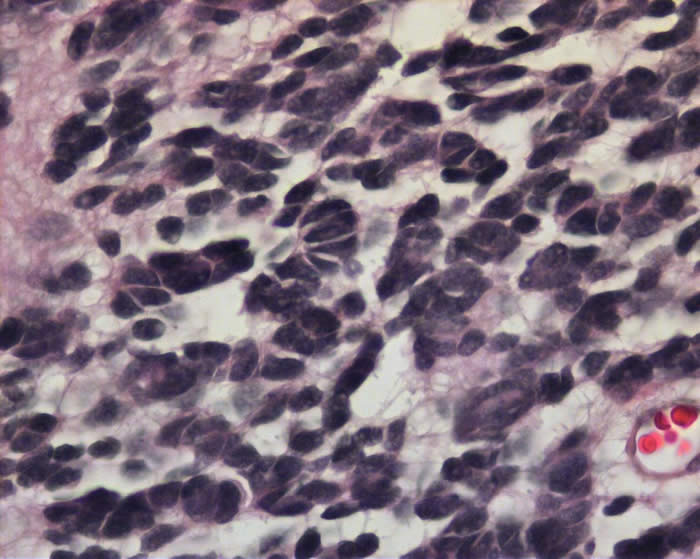
Tumor cells in higher magnification. There are cells with angulated hyperchromatic nuclei. There is cell moulding:
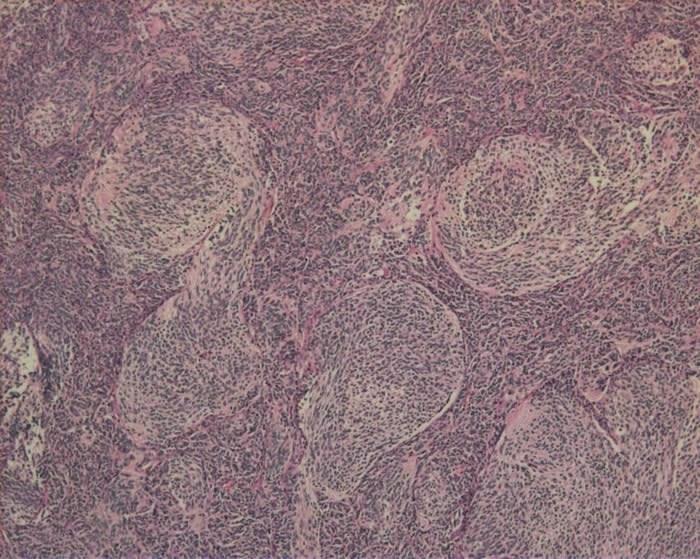
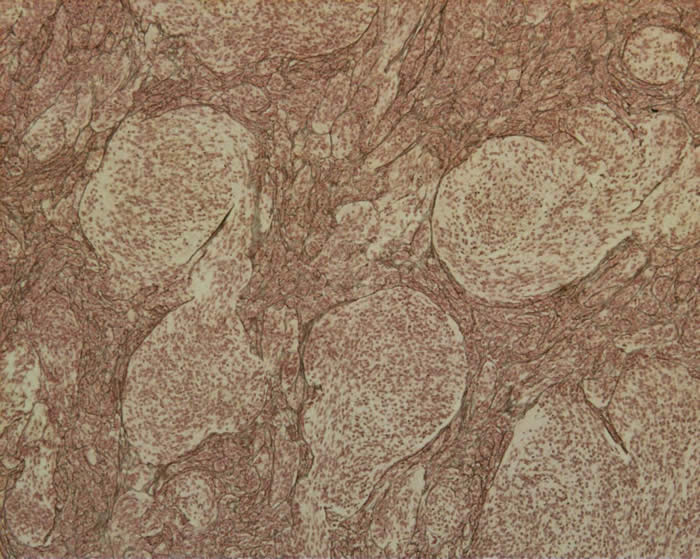
Desmoplastic form of medulloblastoma can be histologically differentiated from the classic form.
- Desmoplastic medulloblastoma is defined by the presence of several prominent nodules or “pale islands” of tumor.
- These areas are of lower cellularity, reticulin–free, show nuclear uniformity and are in a background of collagen-rich, highly-proliferative tumor.
- This form also tends to be more discrete than the classic variety and is often located in the cerebellar hemispheres.
- The degree of anaplasia of the tumor cell may be a predictor of the patient’s outcome.
- Tumors that are well-differentiated and extensively nodular are found to have better clinical outcomes than those with large-cell anaplasia.
Nodular desmoplastic medulloblastoma:
Reticulin staining in the same desmoplastic medulloblastoma. The reticulin surrounds the nodules and is in the internodular areas:
Tumor cells infiltrating through the molecular layer of the cerebellum. Tumor is present in the subarachnoid space: