Duration of symptoms is highly variable (weeks to years prior to the diagnosis) and depends on the type of tumor.
- Diffuse gliomas have a shorter history of neurologic symptoms. In one study the mean duration of symptoms prior to diagnosis was 2.6 months with 77% of patients having at least on cranial nerve abnormality.
- Focal tumors are associated with more prolonged symptoms. On average symptoms are present for 10.6 months prior to diagnosis and cranial nerve involvement is only seen in 29%.
Most Common Signs of Brain Stem Glioma:
- Palsy of the soft palate
- Facial palsy
- Pyramidal weakness.
- Gait ataxia
- Dysarthria
- Difficulty swallowing are also frequently observed.
Tectal Lesions
- Often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Diplopia (due to involvement of the medial longitudinal fasciculus).
- Nystagmus, oculomotor paresis, and eyelid retraction are also symptoms associated with these tumors (involvement of cranial nerves III and IV).
Signs of increased intracranial pressure
- Less common in children than in adults.
- Papilledema = optic disc swelling secondary to raised intracranial pressure.
- Headaches and hydrocephalus tend to occur when tumor involves the periaqueductal or fourth ventricle outflow areas.
Medullary involvement
- Causes bulbar signs, which include difficulties in swallowing and feeding.
- Other signs include asymmetry of the palate, an absent gag reflex, atrophy of the tongue, and nasal regurgitation of food.
This 2 year old boy presented with a short history (one to two months only) of lower limb weakness, difficulty swallowing and signs of a respiratory tract infection. The sagittal T1 MR below shows a tumor (#1) expanding the medulla oblongata. The lesion is pushing the pons superiorly.
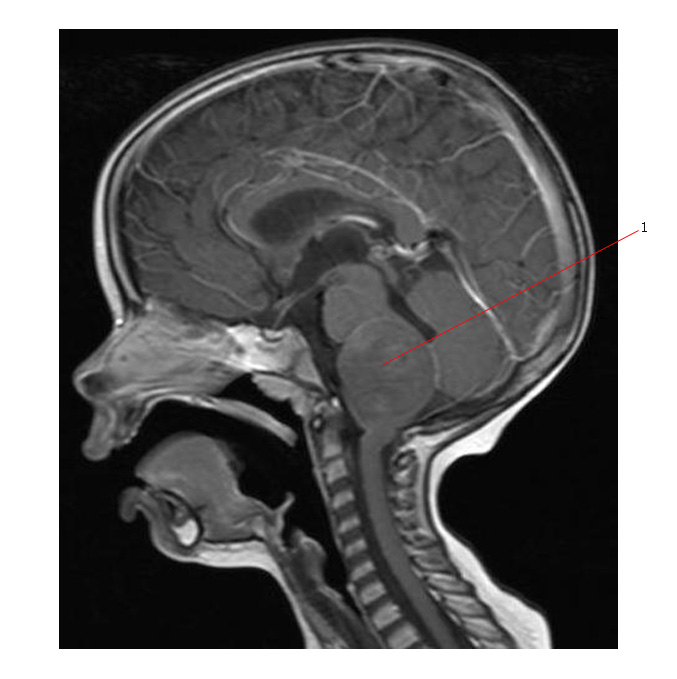
This is the same tumor (#1) below - it has high intensity signal on T2 axial scan.
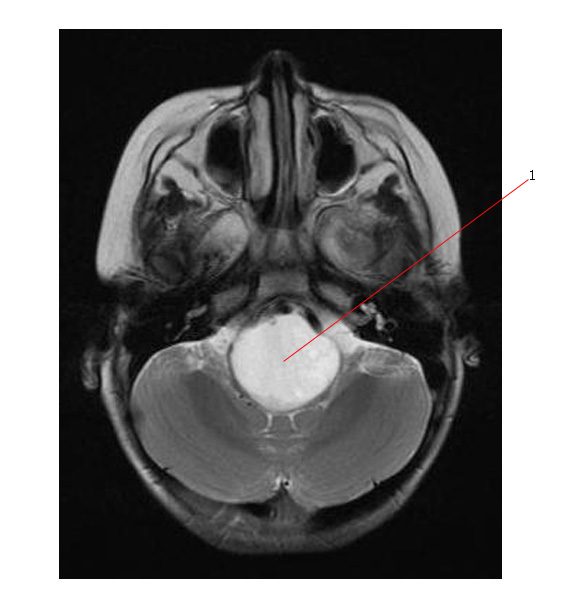
Below the MR shows that this tumor (#1) has early enhancement on post Gadolinium T1 axial scan.
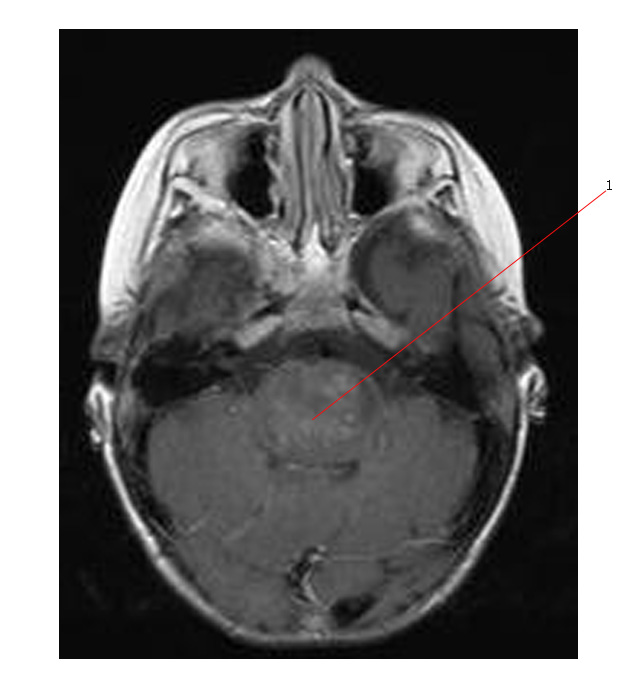
This tumor was a high grade diffuse brain stem glioma.
Cerebellar dysfunction
- Linked to motor abnormalities.
- Limb ataxia is a common symptom.
- These motor difficulties may also reflect the involvement of the corticospinal tracts.
Infants affected by a pontine tumors
- Often appear emaciated and have profound failure to thrive.
- May have facial paresis.
- Often lack the cough response during suctioning, display a depressed gag reflex, and exhibit respiratory irregularities.
Personality changes may also be observed in older children with pontine tumors.
Table : Brain areas involved and associated symptoms
| Brain area involved | Associated Symptom(s) |
| Tectum | Headache Nausea Vomiting Diplopia Eyelid retraction Nystagmus |
| Cervicomedullary area | Loss of sensation in the face
Dysphagia Ataxia Oculomyoclonus |
| Medulla | Difficulties in swallowing and feeding Asymmetry of the palate Absent gag reflex Atrophy of the tongue Nasal regurgitation of food |
| Cerebellum | Limb ataxia |
| Ventricular locations | Hydrocephalus |
| Pons | All of the above, as well as: Palatal palsy Dysarthria Drowsiness Head tilt Deterioration of hand writing and speech |

