MR scan
This is the optimal imaging modality for these tumors.
MR shows disease extent more accurately than CT
- Clearly identifies the lowest portion of disease (best seen on coronal and axial planes and not shown well on CT).
- Sagittal plane is most effective at evaluating pontine involvement.
Tumors usually have:
- Decreased signal on T1-weighted images.
- Increased signal on T2 weighted images.
MR can differentiate between diffuse and focal pilocytic tumors:
- Diffuse tumors appear as poorly differentiated regions of increased intensity on T2 imaging.
- Pilocytic tumors are better circumscribed and can be exophytic.
Ring-enhancement patterns with gadolinium are sometimes seen:
- Contrast enhancement in half of all cases, often being focal or nodular.
- The presence of contrast enhancement alone does not give any indication of the tumor type or grade.
Cysts are not common within the tumor, but the tumor may have a heterogeneous appearance.
Common feature is anatomic distortion of the pons.
Invagination or enlargement of the basilar artery is also often observed, as well as total effacement of the prepontine cistern.
Leptomeningeal seeding in this disease is extremely rare.
The axial MR below is very typical for a brain stem glioma (#1) with diffuse involvement of the pons:
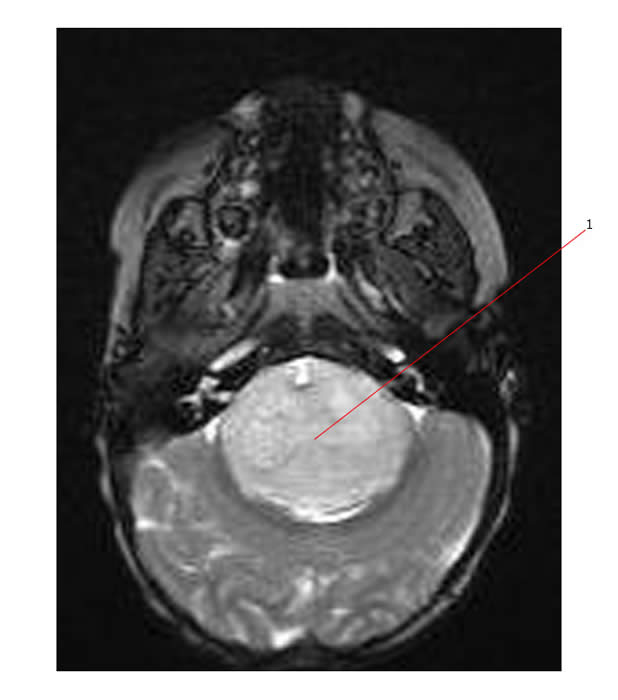
The scans below are axial and sag. MR scans of a brain stem glioma. #1 points to a tumor diffusely involving the brain stem.
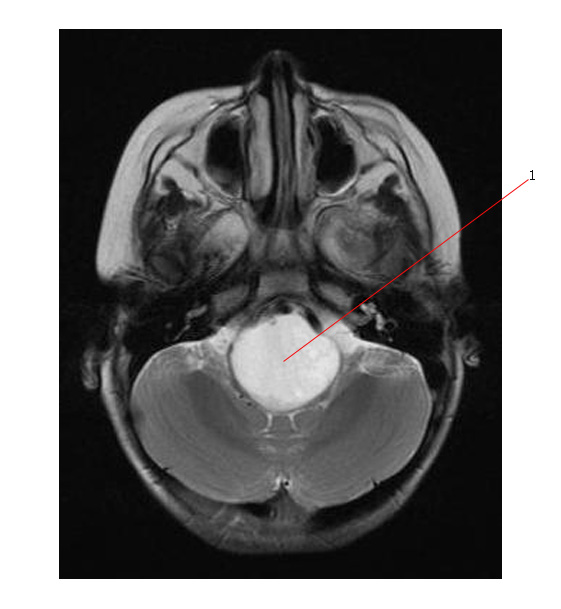
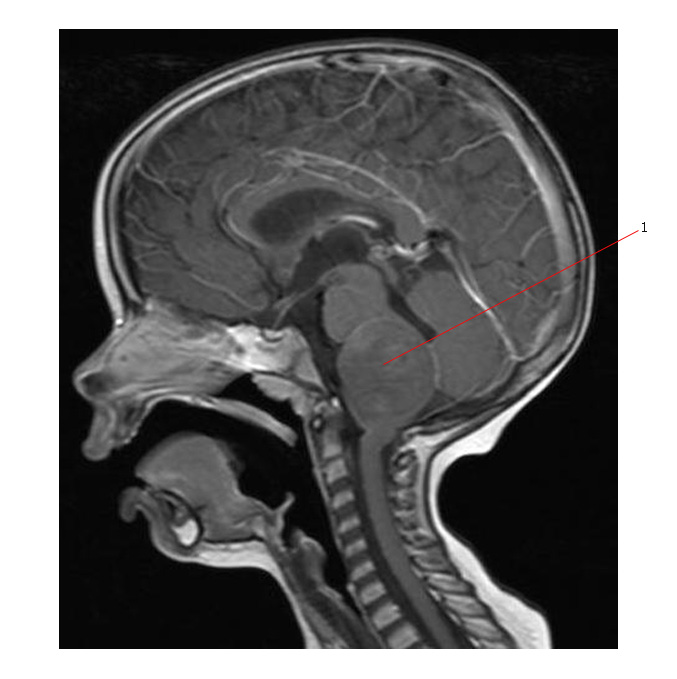
Abnormal signal intensity in the pons may be due to several other etiologies - but it would be very unlikely that these would cause the diffuse swelling seen on the MR scans above.
The differential diagnosis can include:
- Encephalitis.
- Demyelinating disease.
- Cavernous angioma and arteriovenous malformation.
CT Scan:
- Can be useful for the initial diagnosis and post-operative follow-up.
- Can identify calcification and displacement or distortion of the ventricular system.
- Can show those tumors that are cystic or exophytic, but is unable do distinguish benign from malignant tumors.
- It can image the extension of the tumor into the cerebellar peduncles and hypothalamus.
- CT definition is highly dependent on the recognition of altered anatomy. There are certain features that are commonly observed using CT, and their relative frequencies in the population are determined:
Link:


