History and Physical Examination:
A complete history and general physical exam should be performed.
This should include a detailed neurologic examination for cranial nerve palsies and motor/sensory deficits.
Fundoscopy:
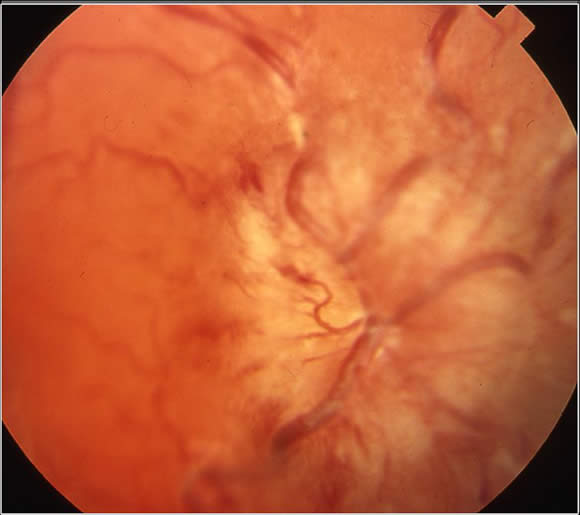
A funduscopic examination may show signs of increased intracranial pressure (papilledema).
The picture below shows papilledema with swelling and hemorrhage involving the optic disc:
Radiology:
- Modern radiologic imaging techniques are essential.
- MR of the brain is the standard investigation used to make the diagnosis of diffuse brain stem glioma.
- CT scan can also be helpful.
Biopsy:
Biopsy is not commonly pursued in the diagnosis of diffuse brain stem gliomas:
Significant risks are involved in biopsy of a diffuse brain stem glioma – any bleeding in the brainstem or damage to critical tissue can lead to death or major neurological damage.
There is no consistent correlation between tumor histology and outcome and pathology does not influence treatment.
The presence of a diffusely infiltrating pontine glioma on MR scan is far more indicative of patient prognosis than the histology of the tumor. Regardless of the histology, all diffuse tumors show poor duration of response to radiation, with a median survival of less than 1 year after treatment.

