Infection
Patients are at risk of life threatening infections immediately after transplant due to prolonged neutropenia.
Most severe infections present as fever with signs of systemic inflammatory response syndrome. For example:
- Hypotension
- Tachycardia
- Respiratory distress
- Edema
- Encephalopathy
Admission to intensive care is not uncommon.
Common infections (bacterial, viral, fungal) during the aplastic phase include:
Infectious Agent |
Risk Factors |
Gram-Negative Bacteria |
|
Staphylococcus epidermidis |
|
| Viridans Streptococci |
|
RSV, Parainfluenza and Other Respiratory Viruses |
|
Clostridium difficile diarrhea |
|
Candida species |
|
Aspergillus |
|
Herpes Simplex Virus |
|
Most patients receive prophylaxis with :
- Acyclovir (if they were previously exposed to HSV)
- An anti-mold azole (e.g. itraconazole, voriconazole).
Antibiotic prophylaxis is controversial.
Fever in the HSCT patient is a medical emergency and requires prompt attention including
- Full patient assessment
- Blood cultures
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics (usually pipercillin-tazobactam with an aminoglycoside such as gentamicin but this will differ by institution)
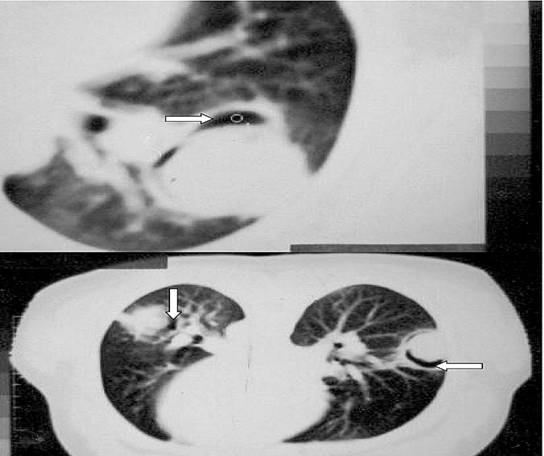
Anti-fungal agents (usually liposomal amphotericin) are added if fevers continue for more than 3-5 days and an evaluation by computed tomography of the chest to look for pulmonary aspergillosis is undertaken.
Figure: Bilateral pulmonary aspergillosis in a patient two weeks after an allogeneic unrelated HSCT. Note the presence of the “halo sign” on the CT scan. Patient had been having fevers for 4 days and increasing respiratory distress.