The initial approach would always involve surgery and as complete a resection as possible if deemed to be safe.
A comparison of Parenchymatous Pinealoma:
Pineoblastoma |
Pineocytoma |
|
Age |
Young |
Adult |
Speed of progression |
Fast |
Slow |
Length of illness |
Short |
Long |
Expansion |
Infiltration |
Compression |
Spread in CSF |
Common |
Rare |
Cytoplasmic processes |
Few |
Many |
Type of rosette |
Homer-Wright |
Pineocytomatous |
Giant cells |
Present |
Present |
Histologic variants |
Subtle |
conspicuous |
Pineoblastomas
- A type of Supratentorial Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (supratentorial PNET).
- Treated with a combination of chemotherapy and RT after surgical resection if this is possible.
- High risk medulloblastoma protocol generally used (for example - 36 Gy to the craniospinal axis with a boost to primary tumor to a total dose of 55.8 Gy in 180 cGy fractions plus concurrent chemotherapy).
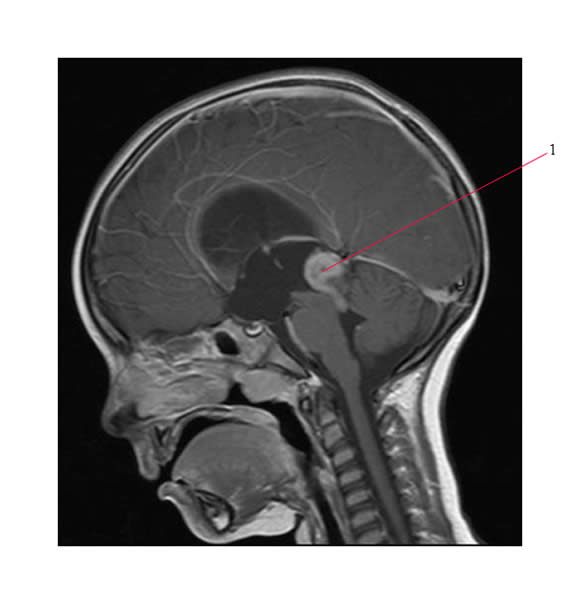
Below is a MR scan of a 3 year old boy with a localized pineoblastoma (#1). Treatment involved surgical resection, followed by intensive chemotherapy (and autologous transplant) and then local radiation therapy (RT). Craniospinal RT would have been associated with significant longterm morbidity.