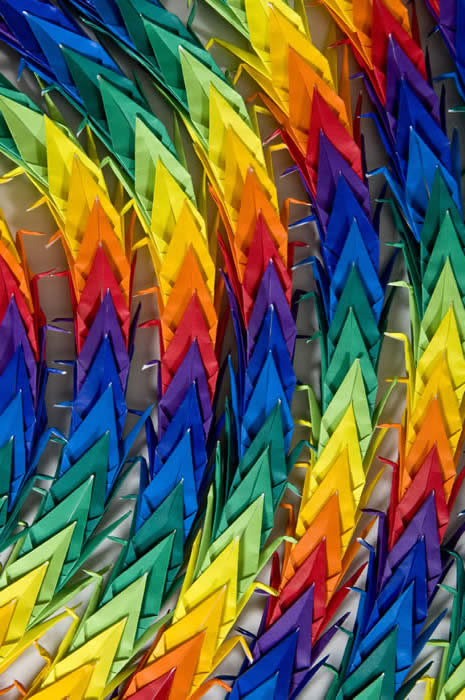
Bone scan
Bone scans are used to evaluate distant skeletal metastases much less frequently because of the accuracy of MIBG scans. However, this can be a reliable investigation to evaluate osteolytic lesions
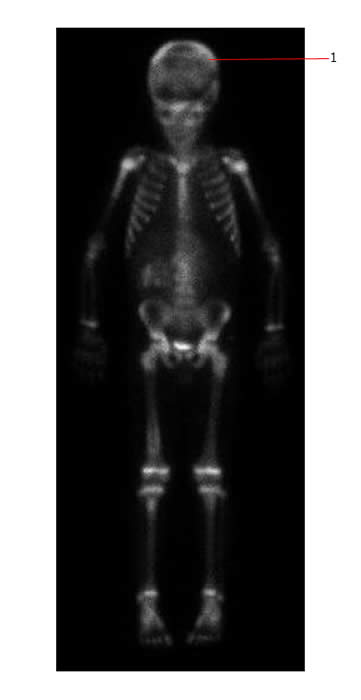
The bone scan below shows extensive diffuse and focal uptake throughout the skeleton consistent with multiple bone deposits in a case of neuroblastoma. The skull (#1) is especially involved as are the proximal humeri and the spine.
MIBG scan:
I-Meta-IodoBenzylGuanidine is taken up by adrenergic secretory vesicles and is handled by the cells in the same way as norepinepherine. It is radiolabelled using I-131. In most neuroblastoma patients it is taken up both in the primary site and metastatic deposits.
- MIBG scan has better sensitivity and specificity than a bone scan.
- Used in diagnosis and to monitor response to therapy
- However 10% of neuroblastoma patients do not have MIBG avid tumors.
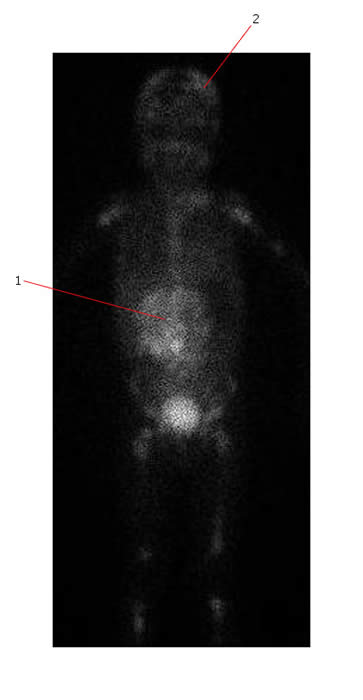
MIBG below shows extensive disease with multiple focal and diffuse increased areas of activity involving the skull (#2), long bones, the whole spine and the pelvis in the same patient. There is also a large area of increased activity in the mid abdomen (#1). This is his primary tumor.
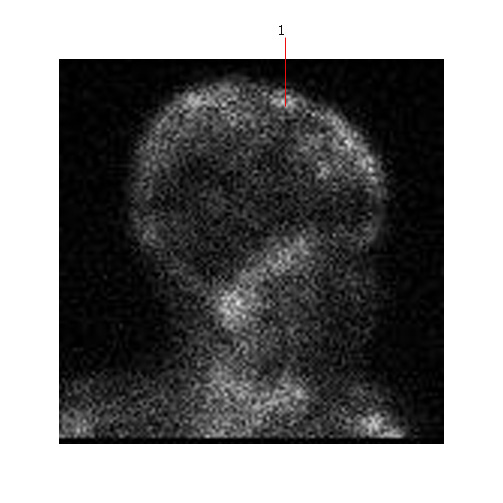
Below is a MIBG scan showing diffuse skull metastases (#1)
Radiolabeled metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) is a highly sensitive and specific marker for detecting neuroblastoma. A semiquantitative mIBG score (Curie score [CS]) is a prognostic indicator for patients with high-risk metastatic disease.
PET scan:
There is uptake of a radioactive glucose analogue 18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose (FDG) by rapidly proliferating cells undergoing anaerobic glycolysis.
In the future PET scanning may be an important investigation to stage and monitor response to therapy in neuroblastoma.
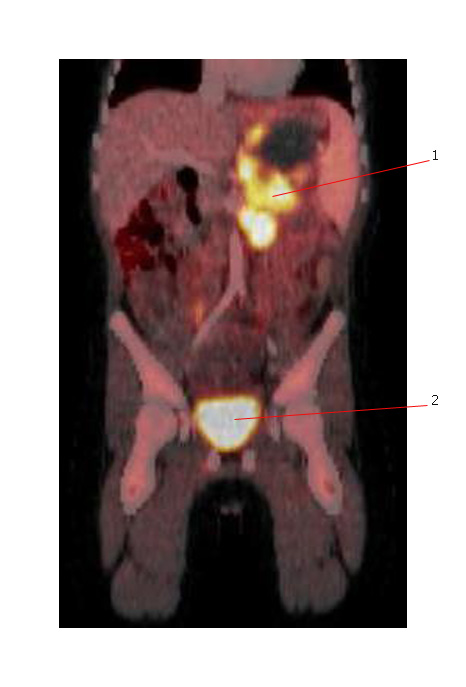
The PET scan below shows avid FDG uptake in a primary neuroblastoma (#1) within upper abdomen. #2 denotes the normal bladder.
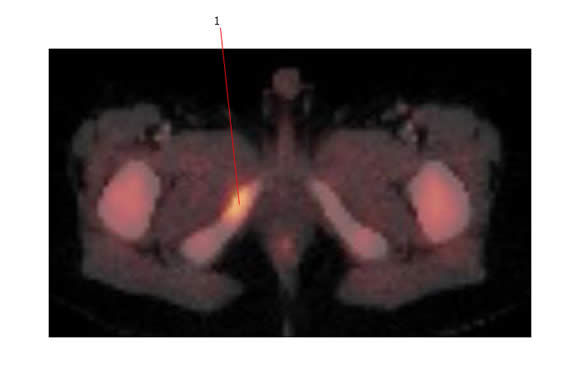
The PET scan below shows FDG avidity in a metastatic deposit from neuroblastoma involving the pubic ramus.
For a review of neuroblastoma imaging:


