Childhood brain tumors may present in many ways, but there are some common features which should alert the clinician to the possibility of a brain tumor:
Children may present with:
- Signs and symptoms of raised intracranial pressure
- Localizing signs
- Non-localizing signs
General Overview of CNS Tumor Presentation:
| Problem | Possible Presentation |
Headache, vomiting, lethargy |
|
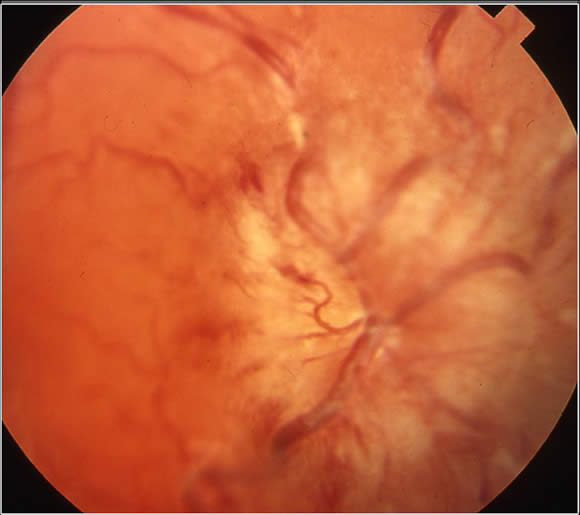
Papilledema - with swelling and hemorrhage of the optic disc on fundoscopy:
|
|
Cranial nerve abnormalities:
The most commonly 6th (VI) cranial nerve palsy:
This is a "false localizing sign".
Hydrocephalus causes compression of the 6th cranial nerve at the petroclival ligament, resulting in diplopia, medial deviation of the affected eye and lateral gaze paresis.
Left lateral rectus (6th cranial nerve palsy)
|
|
Localizing symptoms and signs due to tumor infiltration into normal structures |
Optic pathways:
|
Cerebellum:
|
|
Brain stem:
|
|
Supratentorial brain:
|
|
Deep midline tumors:
|
|
| Non-localizing symptoms and signs | Seizures
General malaise Changes in behavior Loss of previously acquired developmental milestones |
Specific tumor types usually present in characteristic ways which depend for the most part on tumor location.
General Overview of the presentation of common types of pediatric brain tumor:
| Tumor Type | Location | Presentation |
Medulloblastoma |
Posterior fossa | Tumor grows rapidly - short history of illness.
Raised ICP causes: Headache, vomiting, lethargy
Localizing signs: Tumors arise in the cerebellum and are associated with loss of balance (ataxia, tremor and problems with co-ordination)
|
Ependymoma |
Usually posterior fossa | Raised ICP causes: Headache, vomiting, lethargy
Localizing signs: Tumors arise in the cerebellum and are associated with loss of balance (ataxia, tremor and problems with co-ordination) |
| Intrinsic Diffuse Brain stem glioma | Usually brainstem is diffusely involved (often the pons) | Tumor grows rapidly - short history of illness.
Cranial nerve palsies (6th nerve palsy is quite common) Limb weakness (long tract signs) Loss of co-ordination (not prominent)
|
| Focal Brain stem glioma | Focal brain stem involvement | Much longer history than the diffuse brain stem tumors.
Difficulty swallowing (repeated episodes of pneumonia)
Nystagmus and some loss of co-ordination. |
| Optic pathway glioma | Involvement of the optic nerve or chiasm or hypothalamus | Longer history of Visual defects
Nystagmus
Diencephalic syndrome |
| Pineal tumors | Dorsal midbrain involved | Parinaud's syndrome |