Hyperleucocytosis
An increase in circulating leukemic blast cells leads to leukostasis in vital organs.
Hyperleukocytosis is defined as having a white blood cell count over 100,000 x 109 per litre. (Definition = WBC > 100 000 x 109 per litre).
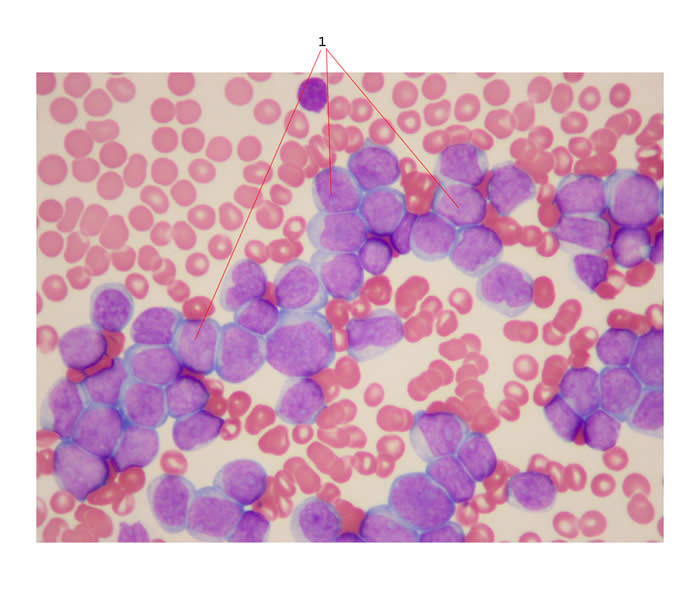
Leukemia causes a very high proportion of circulating leukemia cells (called 'blasts' and examples of these cells are labeled as #1 in the blood film below).
Clinically significant hyperleucocytosis:
- WBC > 200 000 in AML
- WBC > 300 000 in ALL
AML blasts are larger than ALL blasts and are also 'stickier', which is the reason why a lower number of AML blasts can cause problems.
A high white cell count causes hyperviscosity due to:
- sum of packed leukocyte and erythrocyte volume
- reduced deformability of blast cells
The increased viscosity causes obstructed circulation which causes sludging through vessels, and can lead to damage of the vessel walls. This can result in vessel rupture and bleeding.
The areas of the body where these changes in blood vessels are most problematic for a high white cell count are:
- Brain
- Lungs (causing inability to oxygenate and ventilate).
- CNS - sludging can result in a spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage.
Signs and Symptoms:
Intracerebral and pulmonary circulation most commonly affected
- CNS
- change in mental state
- seizures
- headaches
- papilloedema
- Respiratory
- dyspnoea
- hypoxemia
- right ventricular failure
- bilateral 'fluffy infiltrates' on chest x-ray
- Other
- renal failure
- priapism
- dactylitis
Management - General measures
All patients with newly diagnosed leukemia should have:
- Hyperhydration (2 to 3 x maintenance fluids)
- Tumor lysis precautions should be maintained
- Platelets should be transfused to keep levels above 20, as there is a high risk of CNS bleeding.
- Keep platelets > 20
- Correct coagulopathy if necessary
- Patients often quite anemic - and packed cell transfusions should be avoided if possible in patients with very high white cell counts (over 200,000).
- Hb should not be raised > 10g/dl
- Avoid diuretics
Management - Specific Measures
Exchange transfusions or leukophoresis to rapidly reduce the white cell count.
- Leukophoresis
- Exchange transfusion
BUT….
- No studies confirming efficacy
- Rapid rebound in leucocyte count
Start anti-leukemic therapy as soon as patient stabilized

