Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML)
This is a chronic myeloproliferative disorder
Rare disorder - about 4/million annual incidence in North America
Affects young children (over 95% of cases diagnosed before age 4)
15% of cases associated with Neurofibromatosis type 1
Children usually present with:
- Splenomegaly
- Lymphadenopathy
- Skin rash
Peripheral blood:
Immature myeloid precursors (myelocytes, promyelocytes, and myeloblasts) present in the peripheral blood:
- Leucocytosis - elevated white blood cell count > 13 x 109/L (corrected for nucleated red blood cells)
- Monocytosis (absolute monocyte count > 1 x 109/L - corrected)
- Thrombocytosis (variable degree of left shift)
- Circulating nucleated red blood cells
- Usually have elevation of fetal hemoglobin (HbF)
Bone Marrow:
- Hypercellular marrow with mildly increased M:E ratio (typically 5:1)
- < 30% blasts
No Ph chromosome is ever present on cytogenetic assessment
Therapy:
- Intensive chemotherapy alone and trans retinoic do not give a durable remission
- Complete remissions have only been achieved with stem cell transplantation
Below is the image from Nature at : www.nature.com/.../v21/n5/fig_tab/2404596f1.html
Bone marrow aspirate in Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML):
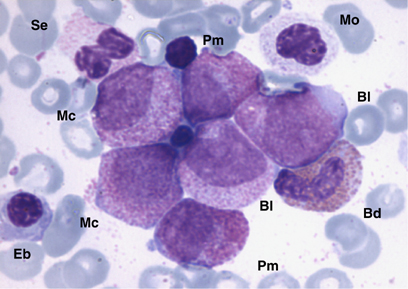
Morphology of JMML. Bone marrow smears were stained with May–Grünwald-Giemsa and shown at 1000-fold magnification. Bd=band, Bl=myelomonoblast, Eb=erythroblast, Mc=myelocyte, Mo=monocyte, Pm=promyelocyte, Se=segmented neutrophylic granulocyte.
External Links:
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia at the National Cancer Institute

