Central Nervous System
Meningiomas
After cranial radiation therapy (RT) there is a significantly increased risk that patients will develop intracranial meningiomas in the long term.
Banerjee et al at the University Hospital of Oulu, Finland reported on a group (60 patients consecutively treated) of long term survivors treated with cranial RT for leukemia as children between the ages of 1 and 8 years9:
- Overall incidence of meningiomas in these patients was 22%.
- No other types of brain tumors were seen in these survivors.
- The following factors did NOT affect the risk of development of meningiomas:
- Age at the time of RT
- Gender
- Chemotherapy (intensity/Rx regime)
- Dose of RT
Risk of meningiomas was strongly linked with the length of follow up.
- Long latency period (mean, 25 years; range, 14-34 years)
- Increasing incidence with time after therapy
- 20 years after the treatment the incidence was 47%
Meningiomas after cranial RT tend to be:
- Multiple
- Atypical
- More likely to recur after surgery
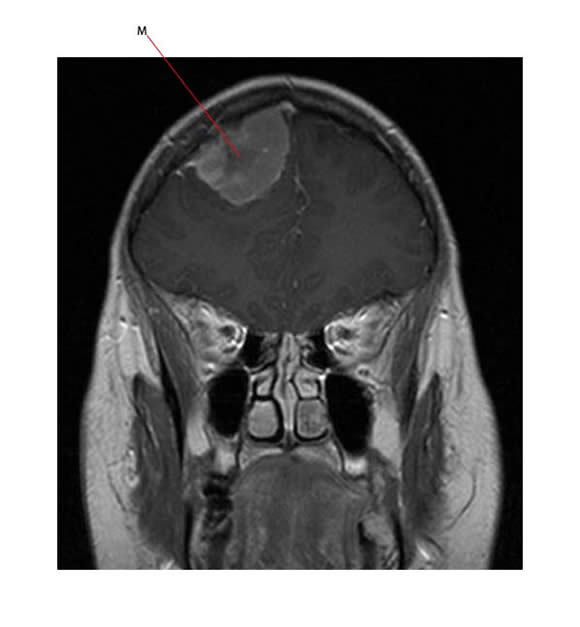
The image below shows a radiation induced meningioma (M). This is a large dural based abnormality which grew slowly in a patient who was given prophylactic cranial radiotherapy for childhood leukemia.
The treatment is surgical whenever possible.

