Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly malignant neoplasm arising from embryonic mesenchyme. It may occur in any anatomic location where skeletal muscle is found.
The International Classification of Rhabdomyosarcoma schema was published as part of the IRS in 1995. Four histologic subtypes were established:
Embryonal (57%):
- Most common type and usually in children less than 10 years old
- Accounts for 75% of all head and neck histology and is the usual type for an orbital primary (accounts for only 30% of trunk primaries and 50% of tumors in other sites).
- Pathology resembles normally developing muscle in the 7 - 10 week old fetus.
- The cells are usually spindle shaped - often mixed with primitive round cell forms.
- Tumor cells are PAS positive (glycogen in the cytoplasm) and under the EM they contain myofilaments - thick (myosin) and thin (actin).
- The differential diagnosis includes lymphoma, Ewing’s sarcoma and neuroblastoma.
Botryoid (6%) and Spindle Cell (3%):
- Less common variants of embryonal RMS with improved prognoses.
- Botryoid RMS arises from the mucosal surfaces of the vagina, bladder, uterus, bile duct, nasopharynx and middle ear. These tumors are generally localized and non-invasive and have a grape like configuration macroscopically.
- Most common primary site for spindle cell RMS is paratesticular.
The slide below shows embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma with a typical small round blue cell appearance.
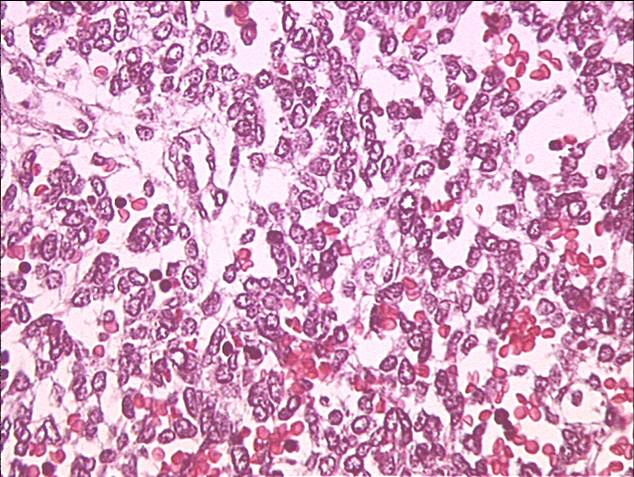
The slide below shows embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma again – sarcoma botryoides appearance in vaginal site
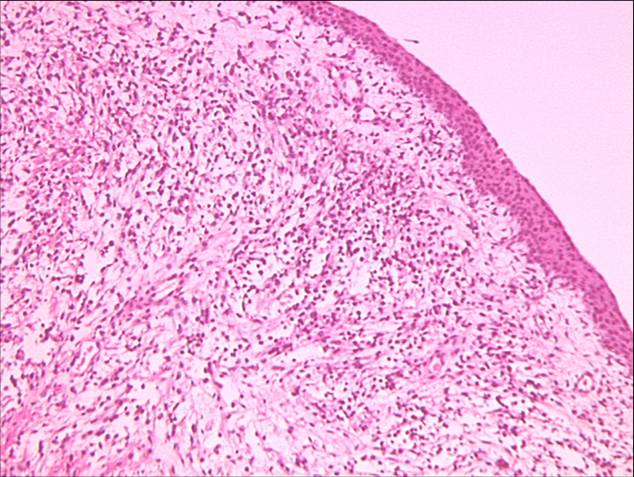
Embryonal RMS at the Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
Alveolar (24%):
- Makes up 20% or so of all RMS and affects older children (adolescents and young adults)
- Has a much worse prognosis than embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
- Most common primary sites are extremities, trunk and perineum
- Tumor resembles developing skeletal muscle in a 10 - 20 week fetus. The cells are round with scanty eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Called alveolar because the cells tend to line connective tissue septae like lung alveoli
The slide below shows alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.
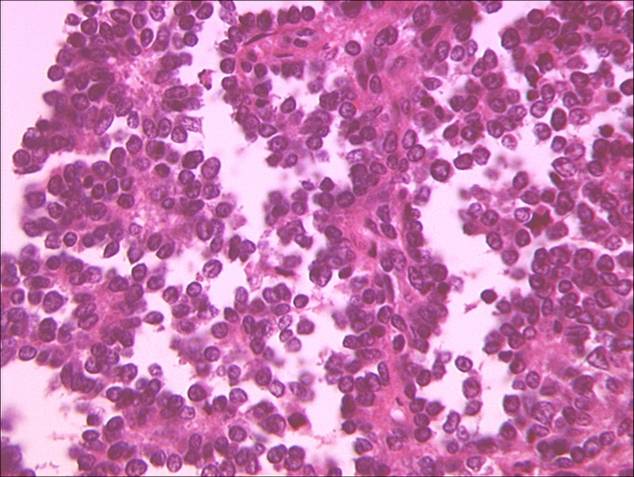
Alveolar RMS at the Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
Undifferentiated sarcoma (3.5%):
- These tumors tend to have a poorer prognosis.
Not Otherwise Specified (6.5%)
- Final category for sarcomas that could not be classified into a specific subtype above.

