Action
Chemotherapy indiscriminately kills rapidly dividing cells.
Malignant cells have limited ability to repair themselves when injured.
Normal cells are more successful at repair
- Bone marrow
- Epidermal cells
- Epithelial cells lining the Gastrointestinal tract (GI), oropharynx
- Hair follicles
Antineoplastic agents are designed to kill rapidly dividing cells
Based on concepts of:
- Cellular kinetics and cell life cycle
- Cell cycle time
- Growth fraction
- Tumor burden
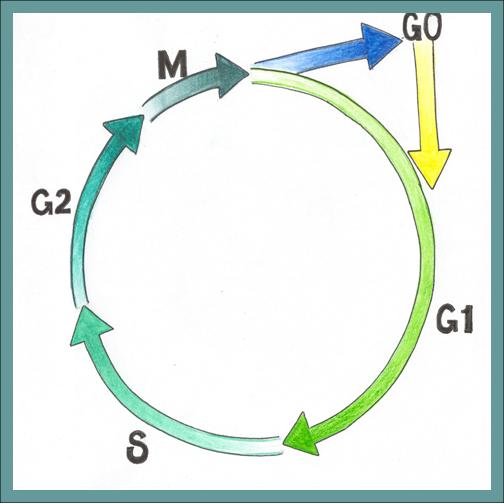
CELL LIFE CYCLE
Gap 0 (G0) = Resting phase. Cells not dividing. Some cells spend little or no time in G0 (eg. epithelial cells, malignant cells)
Gap 1 (G1) = Post mitotic phase. Enzymes necessary for DNA synthesis produced. Protein and RNA synthesis occurs. Time span highly variable, which accounts for the differences in cell-doubling times for different types of cells.
Synthesis (S) = Cellular DNA duplicated
Gap 2 (G2) = Premitotic phase. Precursors of mitotic spindle produced.
Mitosis (M) = Cell division in 4 step process
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
CELL CYCLE TIME
- Amount of time required for cell to move from one mitosis to another.
- Length of total cell cycle varies with specific type of cell
- Length of time spent in G0 varies
- Shorter cell cycle time results in higher cell kill
CELL KILL HYPOTHESIS
- Small percentage of cells killed with each chemotherapy cycle
- Ultimately only a few cells remain which the immune system destroys
- Rationale for multiple cycles of chemotherapy
TUMOR GROWTH FRACTION/ TUMOR BURDEN
Growth fraction = Percentage of cells actively dividing at a given point in time
- Higher growth fraction results in a higher cell kill with cell cycle specific agents
- Higher number in G0 will be more sensitive to cell cycle non-specific agents
Tumor burden = Number of cells present in a tumor
- Cancers with small tumor burden more responsive to therapy
- A high tumor cell burden leads to drug resistance

