Ptosis
Causes include:
3rd Nerve paresis
Causes:
- ptosis >2mm
- exotropia (divergent) and Hypotropia (down)
- limitation of elevation / depression / adduction
- pupil dilated and poorly reactive
- can be pupil sparing
Horner syndrome
Causes:
- 1-2mm ptosis
- pupillary miosis (smaller) but reactive
- lower lid inverse ptosis (leading to apparent enophthalmos)
- may have ipsilateral facial flushing / impaired sweating (anhydrosis)
commonest identifiable cause of an isolated Horners is a Neuroblastoma
Tumour involvement of the upper lid
- commonest tumour involving the eyelid is a capillary haemangioma
- can cause occlusion of the visual axis or astigmatism from compression
Lambert-Eaton syndrome
- rare myasthenia type syndrome
- para-neoplastic
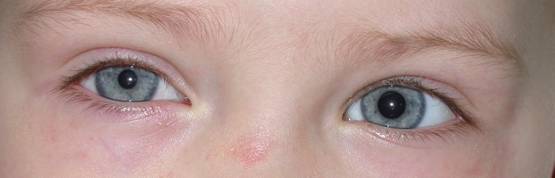
The picture below shows a right Horners syndrome (pupillary miosis, right upper lid small ptosis and lower lid inverse ptosis).
Clinical Tip :
Varying the ambient light can help identify the abnormal pupil.
|

