Photophobia
The causes of photophobia include:
Dry Eye / Keratitis
Any corneal disease leads to photophobia, usually associated with increased tear production and redness. Including corneal toxicity secondary to Ara-C.
Uveitis
Associated with circumcorneal redness, pain/discomfort, reduced vision and sometimes a hypopyon.
Cataract (particularly Posterior Subcapsular)
Scatter of light leads to photophobia. Posterior subcapsular cataracts are located at the nodal point of the eye.
Tumours of the Anterior visual pathway
Optic nerve tumours and chiasmal compression can cause photophobia that may predate any visual loss5.
Meningeal infiltration (eg. CNS relapse of leukaemia / infection)
Shared corneal and meningeal innervation from first division of the trigeminal (5th) nerve leads to photophobia with meningeal irritation.
Raised Intracranial Pressure
Can be associated with:
- headaches
- swollen optic nerves (papilloedema)
- nausea and vomiting
- visual obscurations (transient visual loss with sudden change in posture)
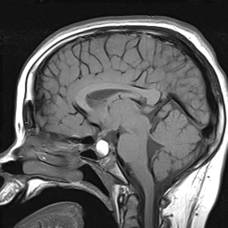
For example: A 13 year old boy presented with a one year history of photophobia and vomiting. He had a normal ocular examination with no optic nerve swelling.
An MRI scan revealed a calcific lesion invading the sella, characteristic of a craniopharyngioma.