Proptosis
Causes include:
Orbital cellulitis
- Commonest cause of proptosis in a child
- Especially to be considered in immunocompromised child
- Proptosis
- Limitation of eye movements
- +/- optic nerve dysfunction (RAPD / decr. vision / colour vision)
Differentiating features to orbital tumour
- Pyrexia / unwell systemically
- Pain (intense)
- Deep bluish-red hue
Orbital tumour
- Can be rapid and dramatic, but less painful and no pyrexia
- Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common
- Other causes include:
- Optic nerve glioma
- Meningioma
- ALL
- Metastases
- Orbital Capillary Hemiangioma
- Medulloblastoma
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis
- Ewing sarcoma.
Clinical Tip :
Differentiating orbital cellulitis from preseptal cellulitis.
|
Clinical Tip :
If the pain seems less than expected for the degree of proptosis, there is a lack of systemic illness and lack of response to intravenous antibiotics then consider imaging to rule out an orbital tumour.
|
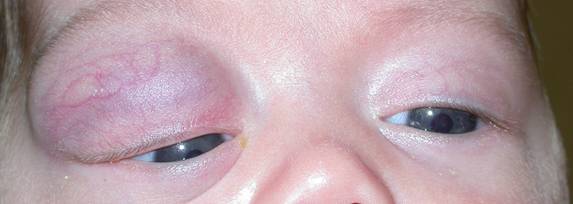
The photograph below shows right proptosis with displacement of the globe down and medially by an orbital tumour
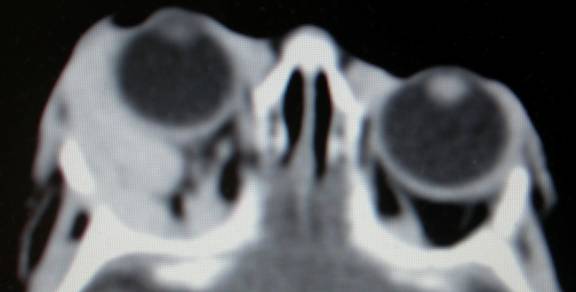
Below is a CT scan of the same child showing proptosis of the right eye by orbital tumour