Skin
Radiation Therapy (RT) Related Damage
RT toxicity is likely to be worse in patients who are:
- Very young
- also the elderly have an increased risk of adverse skin effects
- Diabetic
- Any cause of microcirculatory impairment increases the risk of problems
- Lack of skin pigmentation
- Race (red hair, fair skin) may predispose towards increased late effects (may be related to increased sensitivity to sunlight also in the long-term.
Ataxia-telangectasia is a rare genetic condition where there are predictable, very serious adverse side effects from radiation therapy.
RT related factors:
Damage is more likely with:
- High dose RT:
- Total RT dose tolerance to the skin is 15-20 Gy in unfractionated doses and 30-40 Gy in fractionated doses6
- Treatment volume:
- The risk of late skin effects such as telangiectasia and necrosis increases as the RT volume and dose used increases6
- Treatment technique:
- Orthovoltage (low energy photons) were used to treat many different sites over 20 years ago, but are now reserved only for skin tumor treatment. These low energy photons gave very large doses of superficial RT which would be associated with an increased risk of skin changes
- High fraction size:
- Late skin toxicity is greater when RT is delivered at doses of 2.5 Gy per fraction and above6
Early skin effects from RT6 include:
- Erythema
- Hypersensitivity
- Edema
- Alopecia
- Hyperpigmentation
- Desquamation
These early side effects can be "enhanced" by concurrent chemotherapy1 leading to:
- Blistering
- Necrosis
- Ulceration
- Post inflammatory hyperpigmentation
- Depigmentation
This "enhancement" of the early skin reaction is likely to lead to more severe RT related late effects1.
Chemotherapeutic agents may increase the toxicity of RT if administered within 1 week of each other1
Methrotrexate, actinomycin D, and doxorubicin increase the erythema response to RT6
"Radiation recall" is a reaction that occurs at a previous exposure to RT in which chemotherapy is given triggering an inflammatory reaction. This process is usually reversible within a few weeks of stopping chemotherapy1
Early skin changes progress to late effects over time:
- Erythema appears 2-3 weeks after a standard fractionated RT dose
- Hair loss occurs in dose-dependant way (with threshold of 1Gy) 3 weeks after RT, with hair follicles returning at 9 weeks
- Late skin changes takes months to years to occur
- Latency for fibrosis is 3 years and 5 years for telangiectasia
Long term RT skin effects:
Pathology of RT induced late skin changes6:
- Radiation effects seem to decrease the number of basal epithelial cells and also cause an increased mitotic index in the setting of edema, inflammation, and vascular dilatation acutely
- Changes that occur progressively over time include:
- Destruction of the microvasculature which causes telangiectasia
- Epidermal atrophy
- Dense dermal fibrosis
- Loss of pilosebaceous units
- Atrophic sweat glands
- Progressive arterial and venous lesions
- Radiographic images can consist typically of thickening and increased density of skin and underlying soft tissue6
Changes associated with chronic RT skin damage1,6 include:
- Sebaceous Gland Atrophy
- Dense Dermal Fibrosis
- Telangiectasia
- Loss of hair follicles
- Current recent indicates that RT dose to the hair follicle TD50 of 43 Gy is associated with permanent alopecia6
- Altered Melanin Deposition
- Skin Ulceration
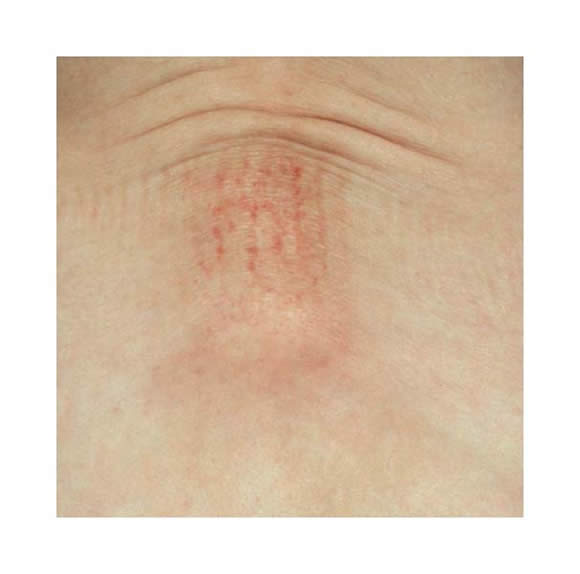
The picture below shows a central area of skin telangectasia, atrophy and mildly increased skin pigmentation associated with previous RT treatment (high dose and large fraction size)