Negligence
Definition
The definition of negligence in medico-legal cases is conduct that falls below the standard established by law for protection against unreasonable risk of harm.
Four major elements are required for a negligence action:
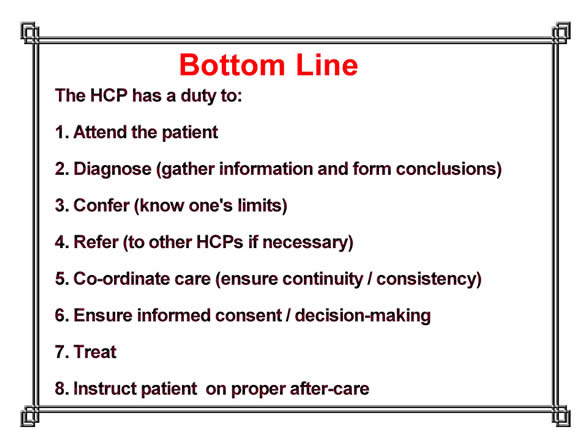
1. Duty - that the health care practitioner (HCP) owes a duty of care to the patient.
2. That the applicable standard of carrying out that duty was breached.
3. Causation (the injury arose as a result of that breach of duty).
4. Injury
There are "Good Samaritan statutes" where the standard of care is changed. A HCP has to be guilty of gross negligence to run into problems.
Duty:
Duty is generally defined by the nature of the professional relationship.
There are different zones of duty for the HCP: